问题来源:
5. Contract modification
A contract modification is a change in the scope or price (or both) of a contract.
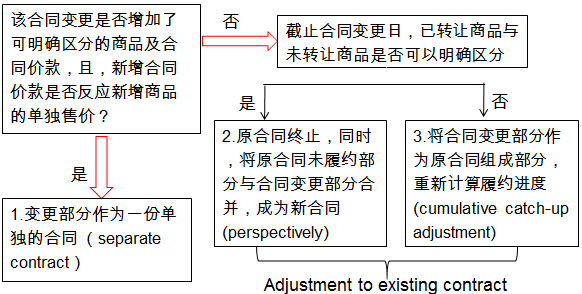
5.1 Modification is accounted for as a separate contract
5.2 Modification is accounted for prospectively合同变更作为原合同终止及新合同订立
5.3 Modification is accounted for through a cumulative catch-up adjustment 合同变更作为原合同的组成部分
Case 1: An entity promises to sell 120 products to a customer for $100 each. Products are transferred to the customer over a six-month period. After the entity has transferred control of 60 products to the customer, the contract is modified to require the dilivery of an additional 30 products to the customer. The additional 30 products were not included in the initial contract.
1. The additional 30 products are priced at $95 per unit. It reflects the stand-alone selling price of the products at the time of the contract modification and the additional products are distinct from original products.
In accordance with IFRS15, the contract modification for the additional 30 products is , in effect, a new and separate contract for future products that does not affect the accounting for the existing contract. The entity recognises revenue of $95 per unit for the 30 products in the new contract
2. During the process of negotiating the purchase of an additional 30 products, the parties initially agreed price is $80 per unit. The entity determines that the negotiated price of $80 does not reflect the stand alone selling price of the additional products.
The new contract cannot be accounted for as a separate contract. Because the remianing products to be delivered are distinct from those already transferred, the entity should accounts for the modification as a termination of the original contract and the creation of a new contract.
Case2: 2019年1月,A建筑公司与客户签订了一项总金额为1000万元的固定造价合同,在客户自有土地上建造一栋办公楼。 2020年初,双方同意更改该办公楼屋顶设计,并因此调整了合同价格和预计成本(总造价增加200万元)。
Answer: The remaining goods and services to be provided using the modified contract are not distinct from the goods and services transferred on or before the date of contract modification. Thus, the contract remains a single performance obligation.
The entity should account for the modification as if it were part of the original contract and update the transaction price and the progress measurement.
2. (March/June 2017 Q3 (c))Carsoon constructs retail vehicle outlets and enters into contracts with customers to construct buildings on their land. The contracts have standard terms, which include penalties payable by Carsoon if the contract is delayed, or payable by the customer, if Carsoon cannot gain access to the construction site.
Due to poor weather, one of the projects was delayed. As a result, Carsoon faced additional costs and contractual penalties. As Carsoon could not gain access to the construction site, the directors decided to make a counter-claim against the customer for the penalties and additional costs which Carsoon faced. Carsoon felt that because claims had been made against the customer, the additional costs and penalties should not be included in contract costs but shown as a contingent liability. Carsoon has assessed the legal basis of the claim and feels it has enforceable rights.
In the year ended 28 February 2017, Carsoon incurred general and administrative costs of $10 million, and costs relating to wasted materials of $5 million.
Additionally, during the year, Carsoon agreed to construct a storage facility on the same customer’s land for $7 million at a cost of $5 million. The parties agreed to modify the contract to include the construction of the storage facility, which was completed during the current financial year. All of the additional costs relating to the above were capitalised as in the financial statements.
Required: The directors of Carsoon wish to know how to account for the penalties, counter claim and additional costs in accordance with IFRS 15 Revenue from Contracts with Customers.
Keryn的思路:
1. penalty and additional cost
2. conter claim (收$)
3. admin. and wastage
4. storage facility ( 价格7,成本5,已完工)
1.列出履约成本资本化条件(直接+提升未来资源+可回收)
penalty and additional cost
wastage
Admin.
2. conter claim 是准则示例中的“unapproved change”
(i)属于modification (ii) no distinct G/S, 因此cumulative catch-up adjust.updating price and process (iii) 由于有Dispute, 要考虑constraint on variable consideration, 综合考虑各种facts,如果达不到极有可能不会发生重大转回,则不能计入交易价格。
3. storage facility 属于modification, 有distinct G/S, 个人认为可以讨论一下是否$7m反映了单独售价。 if yes, separate contract; if no, 原合同终止&新合同开始。 当期已complete, $5m与已履约相关,只能计入当期损益。
Answer: IFRS 15 Revenue from Contracts with Customers specifies how to account for costs incurred in fulfilling a contract which are not in the scope of another standard. Costs to fulfil a contract which is accounted for under IFRS 15 are divided into those which give rise to an asset and those which are expensed as incurred. Entities will recognise an asset when costs incurred to fulfil a contract meet certain criteria, one of which is that the costs are expected to be recovered.
For costs to meet the ‘expected to be recovered’ criterion, they need to be either explicitly reimbursable under the contract or reflected through the pricing of the contract and recoverable through the margin.
The penalty and additional costs attributable to the contract should be considered when they occur and Carsoon should have included them in the total costs of the contract in the period in which they had been notified.
As regards the counter claim for compensation, Carsoon accounts for the claim as a contract modification in accordance with IFRS 15. The modification does not result in any additional goods and services being provided to the customer. In addition, all of the remaining goods and services after the modification are not distinct and form part of a single performance obligation.
Consequently, Carsoon should account for the modification by updating the transaction price and the measure of progress towards complete satisfaction of the performance obligation. A contract modification may exist even though the parties to the contract have a dispute about the scope or price (or both) of the modification or the parties have approved a change in the scope of the contract but have not yet determined the corresponding change in price.
In determining whether the rights and obligations which are created or changed by a modification are enforceable, an entity should consider all relevant facts and circumstances including the terms of the contract and other evidence. On the basis of information available, it is possible to feel that the counter claim had not reached an advanced stage, so that claims submitted to the client could not be included in total revenues.
When the contract is modified for the construction of the storage facility, an additional $7 million is added to the consideration which Carsoon will receive. The additional $7 million reflects the stand-alone selling price of the contract modification. The construction of the separate storage facility is a distinct performance obligation; the contract modification for the additional storage facility would be, in effect, a new contract which does not affect the accounting for the existing contract. Therefore the contract is a performance obligation which has been satisfied as assets are only recognised in relation to satisfying future performance obligations.
General and administrative costs cannot be capitalised unless these costs are specifically chargeable to the customer under the contract. Similarly, wasted material costs are expensed where they are not chargeable to the customer. Therefore a total expense of $15 million will be charged to profit or loss and not shown as assets.

王老师
2021-03-23 16:39:08 1241人浏览
哈喽!努力学习的小天使:
老师在上课时有时为了方便起见会简略写会计科目,并非所有的缩写都是可以在答题上使用的,为了确保得分,建议在答题时尽量使用在书上和真题上出现过的缩写会计科目。
每个努力学习的小天使都会有收获的,加油!
相关答疑
-
2022-08-30
-
2022-07-10
-
2022-07-05
您可能感兴趣的ACCA试题
- 单选题 某投资者一年前以每股40美元的价格购得股票,每年的股息为1.50美元。目前该股的价格为45美元,持有该股票一年的收益率是多少( )。
- 单选题 投资者已经收集了以下四种股票的信息: 股票 β 平均收益(%) 回报的标准差(%) W 1.0 9.5 13.2 X 1.2 14.0 20.0 Y 0.9 8.4 14.5 Z 0.8 6.0 12.0 风险最低的股票是( )。
- 单选题 公司卖出了一个看跌期权,行权价格为$56,同时购买了一个行权价格为$44的看涨期权;购买期权时股票的价格为$44;看涨期权费为$5,看跌期权费为$4,目前的价格上涨了$7,那么ABC公司因为看涨期权取得或是损失的金额为多少( )。








 津公网安备12010202000755号
津公网安备12010202000755号